Shipping from China to New Zealand
Macro handle any kinds of shipment goods from China to New Zealand by sea and by air, such as general merchandise, Hazardous goods, Chemical goods, Out of gauge goods, after got goods information and request from customers, the most important is that our team make the best logistics scheme at first time, so that safe the goods and reduce the cost. Then we provide shipping service from any city in China to New Zealand and we offer competitive shipping freight.
Macro will take care of all your shipping needs. With top of the line and cutting edge technology, we will be your reliable freight forwarder in China to support you in your shipping. Ask now for better shipping rates.

Sea Freight Shipping from China to New Zealand
We are expert to operate the shipping goods from China to New Zealand by FCL, LCL, Bulk-cargo, Roll-Roll under the best shipping freight.

Air Freight Shippingfrom China to New Zealand
Macro provide good air freight for shipment goods from China to New Zealand based on good cooperation with MU, SQ ,HX, CA, D7, CZ.

Door to Door Shipping from China to New Zealand
Macro provide good shipping service and competitive shipping freight for door to door shipment goods from China to New Zealand by sea and by air
FCL Shipping from China to New Zealand
Macro has lower contract ocean freight with shipping line companies from China to any international seaport in New Zealand, especially with OOC, EMC, ONE.
LCL Shipping from China to New Zealand
Macro offers shipping schedule twice per week from any port in China to New Zealand seaport and we charge lower than the market.
More Services When Shipping from China to New Zealand

Cargo Insurance
The cargo insurance protects your goods all the way to any city of New Zealand
Your Best Freight Forwarder from China to New Zealand
- Competitive shipping freight from China to New Zealand by sea and by air
- Provide the best logistics solution
- Free warehouse storage for FCL and LCL shipment goods
- Collect the reasonable local charge to shipper under the FOB trade terms
- Brokerage in China and New Zealand
- Professional product classification and paper work
- Enough shipping space
- Container loading supervision service
- Pick up and delivery service in any city in China
- Rich experiences handle OOG(out of gauge)shipping goods
- Shipping goods tracking and fast feedback
- 24/7 online support
How Long When Shipping from China to New Zealand by Sea Freight and Air Freight
| Port of Loading | Port of Arrive | Transit Time |
| Shanghai | Auckland | 18 |
| Shenzhen | Auckland | 16 |
| Guangzhou | Auckland | 18 |
| Ningbo | Auckland | 20 |
| Qingdao | Auckland | 22 |
| Tianjin | Auckland | 26 |
| Xiamen | Auckland | 22 |
| Dalina | Auckland | 24 |
| China | New Zealand | 1-3days by air |
Shipping from China to New Zealand: The Ultimate Guide
China is a global leader in manufacturing for many reasons, which makes the cost of production low.
For this reason, even if a business is located thousands of miles away, such as in New Zealand, it still makes business sense to source goods from China.
However, it can get a bit tricky, and without understanding all its intricacies, one may run the risk of losing the financial advantage of making such international purchases.
This guide can help you avoid such pitfalls.
I will make the whole process of shipping from China to New Zealand simple and easy for you to understand.
Now, let’s get down to business…
Chapter 1: Top Imports from China to New Zealand
For years, neighboring Australia was New Zealand’s leading importer.
That changed in 2011 when China took over and regularly contends for the top spot.
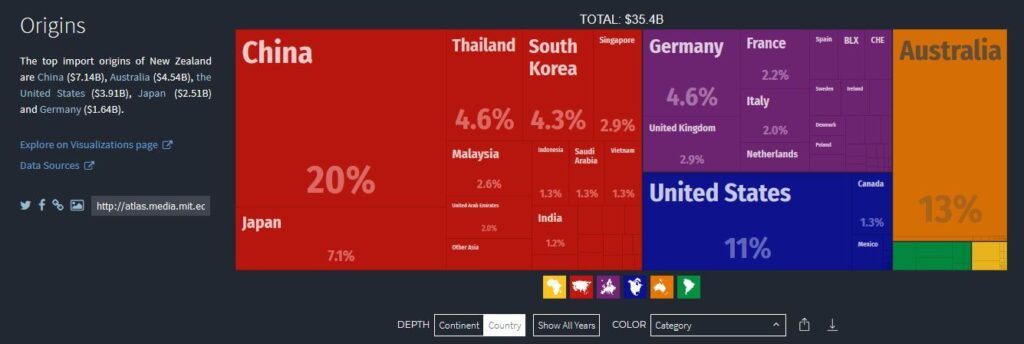
In the decade-long span between 2007 and 2017, trade between China and New Zealand has grown from $8.6 to $26.1 billion.
Trade between the two has been especially boosted by a free trade agreement in force since 2008.
This agreement has seen the two nations work towards significantly eliminating tariffs imposed on each other’s goods.
In 2017, China imported $11.3 billion worth of goods and services, while New Zealand exported to China $14.8 billion worth of goods and services (Unless otherwise indicated, all $ symbols here refer to the New Zealand Dollar).
According to data obtained from the UN’s International Trade Statistics Database, China’s exports to New Zealand include:
- Seafood (mollusks, crustaceans,
- Agricultural Produce
- Electrical machinery
- Vehicles
- Railway locomotives
- Musical instruments
- Lighting
- Firearms, etc.
- China exports more than 4,000 differently coded commodities to New Zealand.
The list cannot be fully listed here.
Machines, clothing and apparel, and China’s top imports, according to New Zealand’s Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade.
Chapter 2: New Zealand Customs Regulations
Getting goods into New Zealand requires clearing with the nation’s Customs Service, which is to be found at all ports of entry.
This declaration isn’t only for goods bought solely for commerce; even personal gifts with a value exceeding NZ$ 110 may be subject to taxes.

- While the primary point of interaction will often be the Customs Service, depending on the nature of the goods you are importing, you may need to deal with, among others:
- Ministry of Primary Industries
- Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade
- Environmental Protection Authority
- Department of Internal Affairs
- Department of Conservation
- Ministry of Consumer Affairs
- Radio Spectrum Management
- Office of Radiation Safety
- New Zealand Police.
This will usually be in the form of securing approval or clearance.
For example, if you want to import radio equipment, you have to clear with the Radio Spectrum Management.
They need to confirm that your equipment won’t be operating on restricted channels.
Similarly, depending on the nature of weapons, you may need clearance from either the police or the Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Trade.
Or both.
2.1 Prohibited and Restricted Imports
Regardless of the import, it is important that you are aware of its legal standing in New Zealand law.
As some goods are totally prohibited or fairly restricted, and could result in legal consequences if one attempts to import them.

The following table shall attempt to list the items that require prior approval from other government bodies before they can be cleared by Customs.
| Ministry Giving Clearance | Goods Requiring approval |
| Ministry of Primary Industries (MPI) | · Most live animals · Meat and edible meat offal from bovines, · Fish including albacore, tuna (long finned, yellowfin, skipjack, bigeye, Atlantic and Pacific bluefin, southern bluefin, etc.), sardines, mackerel, toothfish, yellowtail kingfish, tilapia, carp, salmon, Nile perch, · Crustaceans inc. lobsters, shrimps, prawns · Other aquatic foods including oysters, mussels, mollusks, squids · Dairy produce, birds eggs, natural honey, other edible animal products · Animal originated products not elsewhere specified or included (e.g bones, hooves, beaks, coral, hides) · Live trees and other plants (e.g. onions, tomatoes) · Fruits and nuts (avocados, figs, melons, pineapples) · Cereals · Oil seeds-peanuts, sesame · Fats derived from animals · Crude Sulphur · Peat · Antibiotics (penicillin, streptomycin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, erythromycin) · Veterinary medicine · Fertilisers · Enzymes · Insecticides, fungicides, herbicides · Lab reagents · Plastic tubes, pipes, and hoses · Reservoirs and tanks larger than 300 L · Camping goods · Animal tags · Used pneumatic tyres · Wood and wooden products · Artificial foliage · Used engines · Ovens · Machinery · Railway or tramway equipment · Tractors · Used vehicles · Trailers, semi-trailers, · Motorcycles · Helicopters, airplanes · Marine vessels · Military weapons · Sculptures etc. |
| Department of Conservation (DOC) | · Wild animals (whales, seals, parrots) and meat from wild animals · Trout · Ivory · Fats and oils from marine mammals · C.I.T.E.S. listed items |
| Department of Internal Affairs | · Dogs (live, semen, embryo) |
| Environmental Protection Authority (EPA) | · Aerosol spray · Asbestos · Chemicals Inc. methyl chloroform, HCFC, CFC, · Children’s watercolors set, crayons · Fireworks · Explosives · Insecticides · Fungicides · Fire extinguishers · Used lead acid batteries |
| Ministry of Health | · Tobacco · Nitrous oxide · Controlled drugs · Transformers with PCBs |
| Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MFA) | · Chemicals Inc. arsenic trichloride, sulphur dichloride, hydrogen cyanide etc. (potential precursors to chemical weapons, or toxic chemicals) · Fungicides, herbicides · Diamonds · Mines, cluster bombs |
| New Zealand Police | · Tanks, armored vehicles etc. · Air rifles and air pistols · Revolvers, pistols · Military weapons, mines, cluster bombs · Firearms |
| Ministry of Consumer Affairs | · Cigarette Lighters |
| Office of Radiation Safety | · Uranium, thorium ores |
Food imports tend to require food safety clearance, in addition to other clearances, such as biosafety clearance.
A common biosafety clearance is for brown marmorated stink bug.
Goods coming from the 16 countries listed in the link (Schedule 3) need this clearance, as do goods from Japan.
The focus is especially intense on vehicles, vessels, and machinery.
Regardless of country of origin, yachts, motorboats, and airplanes and helicopters must be cleaned to eliminate the stink bug.
If your cargo contains these crafts from any of the Schedule 3 nations and Japan, it must be treated at the point of origin and then in New Zealand.
It is advised to keep this at-risk cargo separate from other cargo, otherwise, MPI may refuse to clear your ship for unloading.
When dealing with weapons, you will need an arms permit from the Police.
Clearance often involves more than one agency.
Some pesticides and herbicides require clearances from the EPA and the MPI.
Likewise, ivory and whalebone need to be assessed by both the DOC and MPI.
These restrictions are a safeguard against poor quality goods.
Children’s coloring sets are for example tested for toxic chemicals to ensure children are not exposed to them.
The Ministry of Consumer Affairs doesn’t just deal with lighters.
Baby walkers, chainsaws, toys, hot water bottles, ladders, bicycles are some of the goods it approves as conforming to set standards.
- Other prohibitions are set by strictures in the law.
- For instance, you may import any breed of dog, so long as it is not any of the following:
- Japanese Tosa
- Brazilian fila,
- Perro de Presa Canario
- American pit bull terrier
- Dogo Argentino.
Chapter 3: Hire Freight Forwarder to New Zealand
Getting your goods from China to New Zealand often requires a freight forwarder, who shall work the logistics of moving said goods.
A lot of jargon is used around this juncture, with three letter acronyms becoming a regular shorthand of explaining how costs will be split between the owner of the cargo and the seller of the cargo.
To avoid costly confusion, the International Chamber of Commerce came up with INCOTERMS (International Commercial Terms).
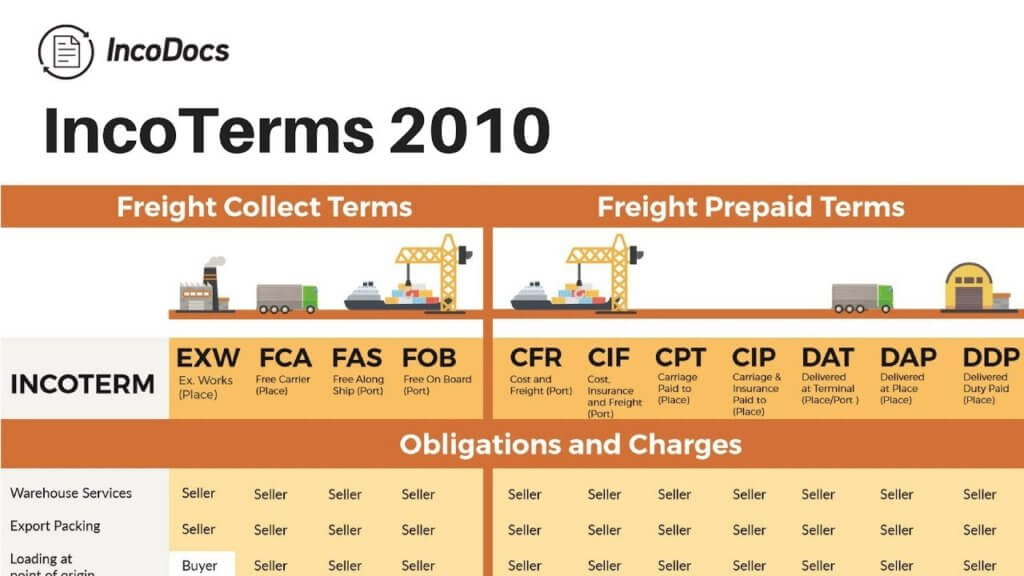
Incoterms just spell out which of the attendant costs involved in getting the goods from the seller to the buyer an ocean away either party is responsible for.
The latest revision of Incoterms was in 2010.
Incoterms shows you which costs you will bear but doesn’t show you how much.

The acronyms explained
· EXW
Ex-works + place.
As soon as the goods have been produced, the seller’s responsibility end.
The seller isn’t even responsible for loading the goods on to the truck that will take the goods to the port.
From that point onward, it’s the buyer who organizes everything.
· FCA
Free Carrier + loading port.
The seller is tasked with delivering the goods up to the stated port of exit.
The buyer is responsible for the cargo from the point of unloading the seller’s vehicle
· FAS
Free alongside ship + loading port.
This is used for bulk cargo.
· FOB
Free on board + loading port. The oldest incoterm, and one you are most likely to hear.
If the quote for your cargo says FOB Shanghai Port, the seller will be responsible for the goods until it is loaded on to space.
This means transport from the factory, customs in China, and other costs in between.
However, you will be the one to book shipping space for your cargo.
You will also be responsible for its delivery to its final destination, and all costs that come after.
This will be freight charges, Customs in New Zealand, storage costs, transport to your facilities, etc.
· CFR
Cost and Freight + destination port.
The seller (in China) caters for the delivery of the cargo up to the desired port of discharge.
The buyer is from that point on responsible.
The buyer facilitates the unloading of the cargo and meets all other costs, such as Customs and transport to their warehouse.
· CIF
Cost, insurance and Freight + destination port. Similar to CFR with insurance added to protect your goods while they are being shipped.
The insurance is paid for by the seller.
CFR and CIF are exclusively used for shipping by sea.
· DAT
Delivered at Terminal + destination.
· DAP
Delivered at Place + destination.
The buyer pays only import taxes and customs clearances.
Otherwise, everything including delivering to the seller’s destination is handled by the buyer.
· CPT
Carried paid to + destination
· CIP
Carriage and Insurance Paid to + destination.
CPT and CIP can be used to describe all modes of transport.
· DDP
Delivered Duty Paid + destination.
The seller is responsible for the goods until they are delivered to the buyer in New Zealand.
All charges, risks, and responsibilities fall upon the seller.
From the above options, if you go with EXW as your option for transferring cargo, and move the cargo on your own, then you will have no need for a freight forwarder.
Truthfully though, it is easier to have your cargo handled by a freight forwarder.
For one thing, most freight forwarders are duly registered to operate within the two countries of interest, in this case, China and New Zealand.
Their established network also help one find the most cost-effective and/or fastest route for your products.
Freight forwarders are likely to be granted discounts by shipping companies.
They will also have the means to track the goods on their way to the destination.
They also come in handy when handling documentation, given their experiences handling international shipments.
As in individual, clearing goods is a time-consuming process, yet freight forwarders can promptly address these, and all at a modest fee.
By the way, here are some useful tips that will help you get a reliable freight forwarder: 7 Tips for Finding a Freight Forwarder in China.
Chapter 4: Air Freight from China to NZ
This is the fastest means of transporting cargo, with cargo reaching the buyer with a day or three, unlike the weeks it would take for a ship.
Its major restrictions are that abnormally shaped cargo which can’t fit in the frame of the plane can’t be transported this way.
Similarly, heavy objects can’t really be transported in bulk this way.
Perishables are almost always transported this way.
The clearance process is similar to that conducted following sea freight, with slight differences emanating from the difference in the mode of transport.
The restrictions/prohibitions are universal to all New Zealand ports of entry, airports included.
Air freight allows goods to reach even remote corners of the country, so long as some airstrip has been created.
Because of its location, Auckland is where virtually all air freight first enters New Zealand.

Local flights are thereafter used to deliver the cargo to its final destination.
Air freight requires airports, so below are major airports in both New Zealand and China.
Major Airports in New Zealand
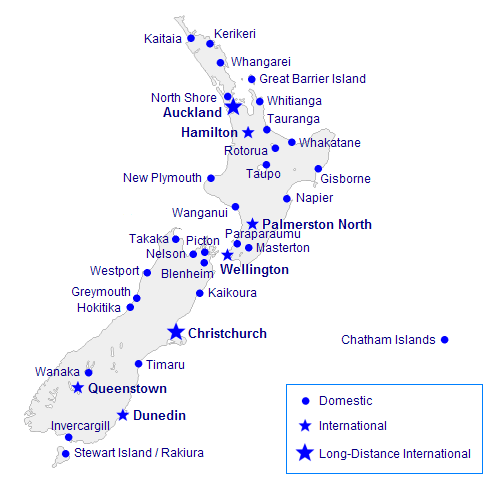
· Auckland Airport
This is New Zealand’s largest and busiest facility, claiming 75% of all international visitors coming into the nation.
It receives nearly 21 million passengers every year.
30 international airlines use this airport as do 4 international freight airlines.
From here, one can connect to 21 local destinations, and there are more than 300 local flights to facilitate this.
Auckland Airport moves in excess of 187,000 tonnes of cargo freight annually.
· Christchurch Airport
Another international airport, the Christchurch Airport serves the South Island and is New Zealand’s second largest.
But it prides itself in being New Zealand’s first international airport.
In 2017, it ferried 6.57 million passengers.
Air freight services also land here, including Air Freight NZ, Airwork and Qantas Freight.
· Wellington International Airport
The third busiest airport in New Zealand, this airport handled slightly over 6 million passengers in 2017.
However, limitations on its runway mean that its primarily used for domestic flights, even if Singapore Airlines regularly flies in.
· Palmerston North Airport
Handling 30 commercial flights daily and 4 cargo flights nightly from Auckland and Christchurch, the Palmerston North Airport doesn’t have scheduled international flights.
It will receive diverted flights from Wellington.
· Other airports in New Zealand
Queenstown International Airport, Nelson Airport, Dunedin International Airport, Hawkes Bay Airport, New Plymouth Airport, Tauranga Airport, Hamilton Airport, Blenheim Airport, Invercargill Airport, and Rotorua International Airport.
Main Airports in China
As expected from such a vast nation, there are more than 200 airports in China.
The busiest, according to a 2018 international survey, are:
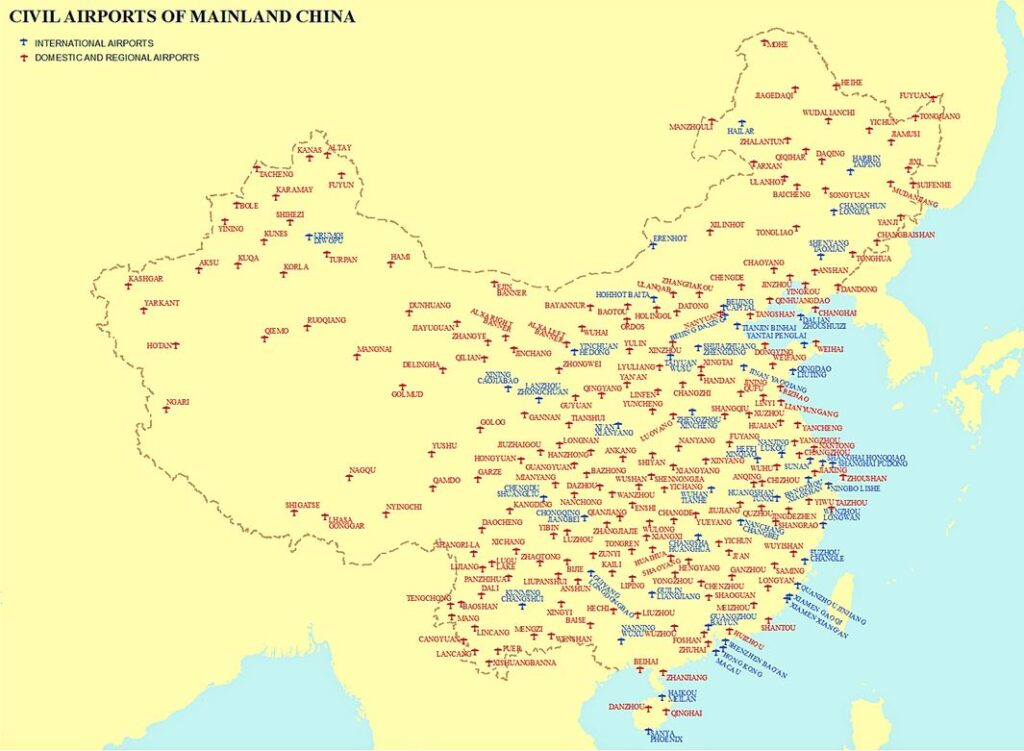
· Beijing Capital International Airport
One of three airports serving the Beijing region, this airport was ranked second in terms of passenger numbers in a global list that was topped by the Hartsfield-Jackson Atlanta Airport in the USA.
There are more than 70 airlines operating from this airport, and some 10 air freight services too.
· Hong Kong International Airport
Sitting on reclaimed land, this airport has, since 2010, held the top spot as the busiest for cargo traffic.
As passenger traffic goes, It is ranked 8th globally.
· Shanghai Pudong International Airport
One of two international airports in Shanghai, this airport is ranked 9th globally with regard to passenger volumes.
It is the major cargo hub for DHL and UPS.
It is the third busiest airport with regard to cargo traffic.
· Guangzhou Baiyun International
Located in the capital of Guangdong province, this airport was ranked the 13th busiest airport globally.
In China, it jostles for the third spot, both with regard to passengers and cargo.
Other major airports are Shuangliu International Airport in Chengdu, Changshui International Airport in Kunming, and the Shenzhen Bao’an International Airport.
Reliable Airplanes from China to New Zealand
Using Shanghai and Auckland, Air China and Air New Zealand provide regular flights between these two cities.
Air New Zealand provides more nonstop flights than the rest.
Other airlines connecting the two cities, and other Chinese cities and Auckland, include China Eastern Airlines, China West Airlines, China Southern Airlines, Hainan Airlines, Tianjin Airlines, Qantas, Sichuan Airlines, Hong Kong Airlines, Korean Air, and Cathay Pacific.

FedEx– Starting life as Federal Express, FedEx is an American multinational company with drop-off points across the globe.
These drop-off locations have been significantly increased with its acquisition of TNT, a former express shipping competitor.
In New Zealand, it has offices in Auckland, Christchurch, and Wellington.
DHL – Believed to be the world’s largest logistics company, especially with regard to air freight, which is handled by DHL Express.
Offices are found in Auckland, Christchurch, Palmerston North, Nelson, Wellington, and Napier.
Besides deliveries made by DHL Express, there’s DHL Aviation in which DHL partners with airlines to make deliveries.
With DHL Express, DHL uses its own fleet.
UPS– More than a century old, United Postal Service has been in New Zealand since 1988.
It’s had a presence in China for a similar period of time and has its major hubs in Shanghai and Shenzhen and more than 200 other facilities across the nation.
From these, it conducts more than 200 weekly flights.
Chapter 5: Shipping Container from China to New Zealand
China’s major seaports are shown in the picture below.
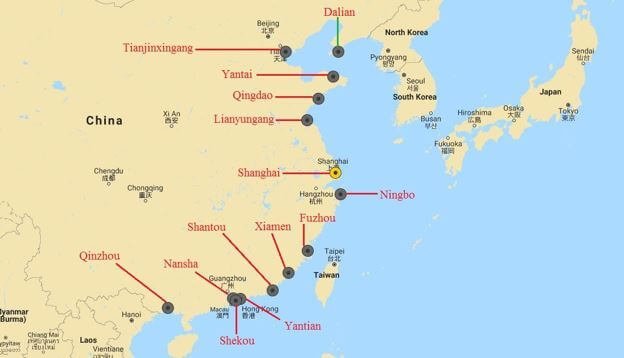
Among the top 20 ports globally, in terms of the volume of cargo handled between 2011 and 2016, are 7 ports from mainland China.
These are Shanghai, Shenzhen, Ningbo-Zhoushan, Qingdao, Tianjin, Dalian, and Xiamen.
Container Shipping Companies from China to New Zealand
i. Maersk
ii. MSC
iii. CMA-CGM
iv. Cosco
v. Evergreen
vi. Hapag-Lloyd
vii. Hamburg Sud
viii. OOCL
ix. UASC
x. NYK
xi. MOL
xii. Hyundai
xiii. K Line
xiv. PIL
xv. Zim
xvi. Wan Hai
xvii. Yang Ming
The top 7 shipping lines above control 65% of global shipping.
Like other transport modes, some of these shipping lines have formed alliances to increase their market share.
There’s the 2M alliance between Maersk and MSC. Hyundai has also joined, and Hamburg Sud acquired by Maersk.
The Ocean Alliance includes CMA-CGM, COSCO, OOCL, and Evergreen.
Hapag-Lloyd, Yang Ming, K-Line, Mol and UASC form what is simply known as the Alliance.
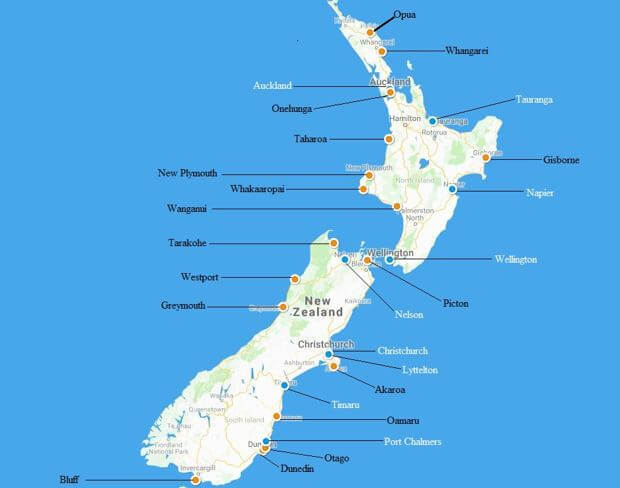
Sea Ports in New Zealand
New Zealand boasts more than 20 seaports but only nine have container terminals, and can thus handle large volumes of international cargo. These nine ports are the Ports of:
- Auckland
- Christchurch
- Lyttleton
- Wellington
- Tauranga
- Port Chalmers
- Napier
- Nelson
- Timaru
- The locations of all New Zealand ports are shown in the map below.
· Ports of Auckland
Located in New Zealand’s most populous city, this port provides excellent shelter and can receive ships longer than 500 ft.
In 2016, it moved 910,000 TEU.
In addition to the container terminal, the port has a multipurpose cargo terminal and inland ports in three locations.
Additionally, it owns companies offering port services, such as Seafuels for marine fuel and North Tugz for pilotage.
Its container capacity was increased in 2017 with the construction of a 300m container wharf.
It has long been the leading port in New Zealand, due to its northern location and its proximity to New Zealand’s most populous city, Auckland.
A breakdown of its trade in 2016 is thus: 907,099 container TEU, 248,065 vehicles, and 5.79 million tonnes of breakbulk goods.
· Ports of Tauranga
Sandwiched between a mountain and an island, this natural port is well sheltered and accessible all year round.
It boasts of 15 berths that can handle liquids, general cargo containers.
It also has two cold storage facilities, and protected storage extending over 2.5 hectares.
This port snatched the crown from Auckland in 2016 when it overtook it for the first time in containers handled, moving about 950,000 twenty-foot equivalent units (TEU).
This may be in part due to the fact that it’s the only New Zealand port capable of handling ships with a load capacity greater than 6,500 TEU.
In recent years the port has been sinking in $350 million expansion program, and it shows.
Two cranes, 13 more straddles have been added, and due to dredging, 9,500 TEU ships can dock in the port.
It is the largest port in the nation, with a bulk terminal, container terminal and an inland container depot located in South Auckland.
It’s handling of 954,006 containers TEU was a 12.1% rise from the previous year’s capacity.
Within the same time, it moved 20.1 million tonnes of breakbulk cargo.
· Port of Napier
Located in Hawke Bay, this port is the second most import-export hub for the North Island.
This is the fourth largest container terminal in New Zealand.
It’s also set to add a wharf.
It handled 257,380 container TEU in 2016, and a breakbulk total of 2.025 million tonnes.
It has ambitious plans, as it was revealed in 2016 that it seeks to increase its container processing capacity.
This would be to the point of making it move more containers than the ports of Nelson, New Plymouth, and Wellington combined.
· Centreport Wellington
Since the devastation caused by the 2016 earthquake (7.8 on the scale), this, the southernmost container terminal port in North Island, has been steadily improving its numbers.
It moved 131,645 container TEU in 2016.
It is New Zealand’s third largest port, even if Wellington is the administrative capital of the city.
Much of it is built on reclaimed land.
· Port Nelson
The northernmost port with a container terminal in South Island, Port Nelson is mostly geared towards exporting the vast riches of South Island-forestry, fish, wine among others.
It lacks a connecting railway. Nonetheless, it handled 96,497 container TEU, in addition to 2.7 million tonnes of cargo.
· Lyttleton Port of Christchurch
With South Island’s largest city, Christchurch, at its back, the port is the main gateway into New Zealand’s third largest city.
It can handle vehicle imports, bulk goods, containers, and specialist liquid imports.
It has two inland ports, one in Woolston, the other in Rolleston.
It has set in motion a plan to dredge its channel, which will allow larger ships access to its facilities.
It moved 361,812 container TEU in 2016, in addition to 678,871 tonnes of breakbulk.
· Primeport Timaru
This port is partially owned by the Port of Tauranga and handles imports of cement, fertilizer, petroleum, and stock feed.
It moved 84,402 container TEU in 2016, an 18.9% improvement in containers handled.
Besides containers, it moved 1.335 million tonnes of cargo.
· Port Chalmers
It’s located on Otago Harbour.
There have been expansion projects in the port, with dredging and extension of wharves either completed or underway.
In 2016, 172,400 container TEU were moved at the port.
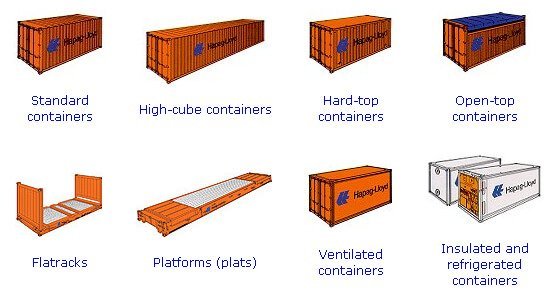
LCL Container Shipping from China to New Zealand
LCL stands for less than container load, and as can be inferred, the goods you are importing don’t fill the container they are housed in.
This container could either be a 20 ft or 40 ft.
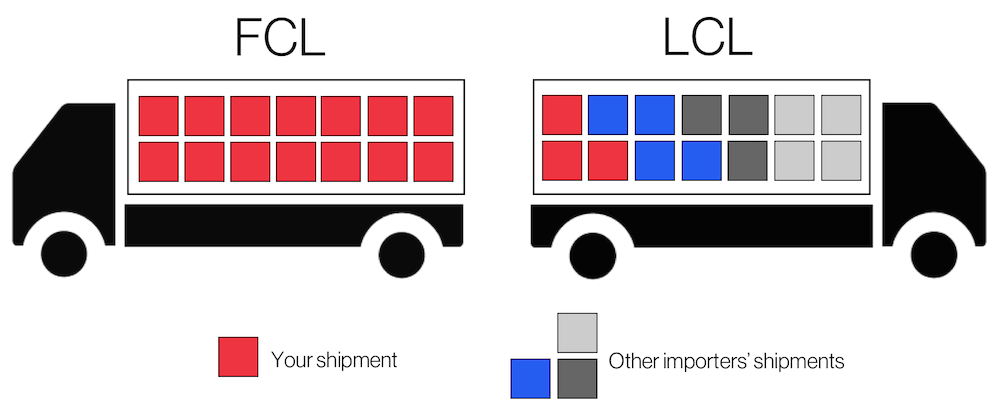
If you go for LCL shipping, then your cargo is housed in a container alongside other businesses/individuals’ cargo.
LCL shipping comes into force if your goods occupy a volume less than half of the container.
You are thus charged for the volume your goods occupy within the container.
The weight can also play a role in determining your cost.
Because your goods are placed with other goods, they are more susceptible to damage if improperly packaged.
All LCL goods are organized in pallets. Preferably these goods need to be housed within sturdy boxes.
If, however, the goods cannot fit in boxes, e.g. furniture, they must be properly wrapped in plastic before place in a palette.
Proper labeling is more critical for LCL shipments.
If there are fragile items, these should be marked prominently; if the goods shouldn’t be stacked, your freight forwarder should be notified.
Dangerous goods are never transported as LCL.
These would include radioactive material, weapons, combustible and explosive compounds.
The challenge with LCL shipments is that it may take time for the container to be fully loaded.
This may delay how fast you receive your goods.
FCL Container Shipping from China to New Zealand
An FCL is a full container load shipment. It is an option taken even without the container actually being fully loaded.
It just means you’ve hired the container exclusively for your goods.
Generally, if your cargo is to be shipped in 12 palettes or more in a 40 ft container, FCL is the option to take.
Ditto with 6 palettes and a 20 ft container.
Because the container is not subject to the troubles of consolidating cargo for different buyers/deconsolidating at the port of arrival, they are less likely to be damaged.
This is especially important when handling fragile cargo.
FCL’s other advantage is that, as a single package of cargo, it is easier to offer port to door services.
By and large, it is considered more cost-effective than LCL.
The process usually begins with receiving an empty container at the supplier’s locations.
The goods are then loaded into the container, following similar shipment preparations as used with LCL.
The loaded container is then returned to the yard for shipping.
FCL can be done in one of four methods.
The first is the Live Load FCL shipping.
The freight forwarder delivers an empty container to the supplier’s premises.
You may get say an hour or two of free loading time.
After this grace period, you are charged for every hour the container remains on your premises.
Alternatively, the freight forwarder will also package your cargo, at a cost.
Within hours, your cargo is containerized and loaded onboard, ready for its journey to New Zealand.
This option is often the most affordable.
Another option is to drop and pick FCL shipping. Sometimes your cargo can’t be loaded within hours; you need more time.
In this method, the freight forwarder leaves the container with the supplier for a few days.
When loaded, the container is then taken to port and onwards.
This method is convenient, but can also be costly, especially if the location is far from the port.
Alternatively, the supplier can deliver the goods to a bonded warehouse.
This is a private facility subject to oversight from customs officials, where goods for import/export can be processed without additional duty charges.
The cargo will then be loaded in containers and delivered to the ship.
Finally, you can opt for port delivery FCL shipping.
With this option, the shipper or freight forwarder handles all issues to the point of delivering the container to your port.
Shipping from China to New Zealand Transit Time
How long it takes for goods from China to land in New Zealand is dependent on a handful of factors.
The speed of the ship is a major factor.
Container ships can go at 25 knots and beyond, but most have taken a steaming approach.
This means they go at slower speeds, almost matching those of the great steamers of centuries gone by.
Consequently, they are likely to move at lower speeds of around 12 knots, because it saves a massive load of fuel and reduces emissions.
Other factors include whether the ship your goods are on will call on ports in other countries, and the condition of the seas.
Generally, though, you should give the shippers at least 20 days.
| Chinese Port | New Zealand Port | Distance | Time at 13 knots | Time at 22 knots |
| Shanghai | Auckland | 6252 nautical miles | 20 days | 11.8 days |
| Wellington | 6552 nm | 21 days | 12.4 days | |
| Napier | 6617 nm | 21.2 days | 12.5 days | |
| Chalmers | 6679 nm | 21.4 days | 12.6 days | |
| Timaru | 6766 nm | 21.7 days | 12.8 days | |
| Lyttleton | 6736 nm | 21.6 days | 12.8 days | |
| Nelson | 6480 nm | 20.8 days | 12.3 days | |
| Tauranga | 6349 nm | 20.3 days | 12 days |
In the table above, the ship’s route went through the East China Sea, followed by the Philippine Sea, and made its way across the Ceram, Arafura, Coral, and Tasman Seas.
This allows the vessel to have ports to call close by in case of an emergency.
An alternative route would be to hit the open ocean after leaving Shanghai, with a route east of the Philippines and Papua New Guinea.
With this route, the distance between Shanghai and Tauranga is down to 5359 nm.
Chapter 6: Alibaba Shipping to New Zealand – A Step-by-step Shipping Process
The first concern people have with making an online purchase is that the product they see posted isn’t what they actually receive; this may be a slight variation in colour to a ridiculously inferior product.
But Alibaba hasn’t grown to be a multibillion-dollar, multinational platform connecting Chinese manufacturers and buyers globally by allowing such instances to prevail.
With due caution, you can get the product you desire. There are several mechanisms to see to it.
For instance, there is a Trade Assurance.
This will help you recover your money if there are delays or issues with quantity and quality.
There are also badges that will tell you about the manufacturer’s capacity, years of trade, and suchlike information.
You could even narrow down the suppliers to those who have dealt with New Zealand clients.
Before you can do all these, you need to create an account with Alibaba to allow you to better interact with these manufacturers.
Conduct a search for the product you wish to import to New Zealand and choose from among the listed manufacturers.
You can opt to narrow down your list of potential suppliers by selecting the desired supplier type.

When you see a product you like, open that tab.
Here you shall see the price and the minimum order quantity.
If you want a sample before committing to the purchase, there is a link to do that.
You can contact the supplier if you wish to negotiate or seek clarification.
If you wish to commit the purchase, click start order to follow through with the processes.
You should have agreed on the unit price, quantity, and payment method.
With regards to payment methods, stick to safe methods such as the escrow service offered by Alibaba, or PayPal, or a line of credit from a bank.
Using other means such as money transfers through services like Western Union exposes you to financial risk with little recourse.

A sample may help you understand if you may require assistance in the form of a shipping broker, so it’s not a bad idea to choose one.
Importantly, you should include in your inquiries matters relating to the shipping of the product.
In most cases, the price is likely to be FOB, and you may have to handle the other bit of getting your cargo from the port in China to New Zealand.
If the supplier has given FOB terms, then it means you need a shipping agent to facilitate the transport of your cargo.
Alibaba also offers logistics services.
The logical next step after settling on the terms of the transaction with the seller is to make the payment and have the supplier deliver the goods as agreed.
The logistics service you’ve chosen will then handle the movement of your cargo, dealing with the necessary documentation and clearances to make sure it arrives in New Zealand.
Chapter 7: Door to Door Service from China to New Zealand

A door to door service means that the seller/manufacturer of the goods you’ve purchased in New Zealand delivers the goods you’ve ordered to the address you’ve given them.
Two main forms of the door to door service exist.
It could be DDP, delivered duty paid, or DAP, delivered at the place, also known as delivered duty unpaid, DDU.
As you may see from the incoterms table above, with the DDP, the manufacturer meets all expenses from factory to your doorstep.
In DDU/DAP, the only expenses to be met by the buyer in this process are the import taxes and other port clearance charges.
Door to door services is intermodal, with ships/planes, rail and/or trucks used by the supplier in concert to ensure a convenient, hassle-free delivery.
Chapter 8: Shipping Cost from China to New Zealand
So, you’ve bought some goods in China and want it delivered to New Zealand; how much will it cost you?
Here’s where a freight forwarder will come in to give you a breakdown of your cost.
Let’s say you’ve gone for Free On Board Ningbo.
You’ve paid for the goods, but then it is up to the supplier to deliver them the port in Ningbo.
Your charges begin with ocean freight, which can be charged per unit area occupied, or per weight.
On Alibaba for instance, you can have charges such as:
US$2-98/cm3
US$10-42/m3
US$1.5-2.0/kilogram
US$200-1000/twenty-foot container.
The prices are on a scale best broken down by the shipping agency, with variability being caused by the nature of the goods.
As an example, perishable goods will require refrigeration while non-perishable goods wouldn’t.
Similarly, cars could be simply loaded in a Roll on roll off Carrier, and this will be a lot cheaper than securing them in containers.
The prices mentioned above usually have a minimum quantity of order.
So, let say your goods weigh 500 kg, and you are being charged US$ 2/ kg.
This will mean getting them on the ship will cost you US$1,000, at least.
If you took other options, say CIF, there would also be the cost of insurance added on top.
This is what it will take to deliver your goods to a port in New Zealand, let’s say the Port of Auckland.
Unless you paid for a whole container, your cargo is likely to be in a container alongside other importers’ cargo.
In Auckland then, someone will be paid to unload the container, and to move your cargo to storage.
If for some reason you cannot immediately unload your container, you have a brief grace period before suffering shipping container detention charges.
These detention charges will add to your cost of shipping.
Then there are charges to be paid to the customs broker (clearing agent), and you have to pay the shipping line and the freight forwarder to get some relevant documentation.
Other charges at the Port of Auckland will include biosecurity inspection by the MPI, which is charged at $120/ hour.
There’s also going to be a customs inspection, and that will cost you, in addition to warehouse handling fees.
Now, if your goods have been warehoused but not yet cleared, you will have 3 days of free storage.
After this grace period is over, you will be charged at a rate of $10 per m3 per day. This is demurrage.
So, if your cargo occupies an area of 20 m2, then every day your cargo is stuck at the warehouse you have a surcharge of $200.
It usually because of these intricacies, and the pitfalls in clearing your goods with customs.
It is often advisable to go with the freight forwarder who will set everything in motion to eliminate or minimize such inconveniences.
Macro Freight Forwarding Services from China to New Zealand
Macro is a freight forwarding company with more than a decade of experience handling all sorts of goods exported from China to other nations, including New Zealand.
With offices in Shanghai, Shenzhen, Guangzhou, and Ningbo, it can quickly facilitate the movement of your cargo.

A pickup and delivery capacity across China, wherever your goods are being sourced from, BanSar can deliver it to you.
Among the perks of choosing Macro as your freight forwarder is free warehousing while your goods are in China for 20 to 30 days.
When your goods have been delivered at the destination port, you have 28 days of free container usage.
With Macro, you can also ensure your goods and have them process your customs clearances.
All freight options are available- sea, air, and land.
With experience in handling conventional cargo as well as out of gauge cargo, hazardous materials, and all sorts of goods, whatever your needs, Macro will provide a fast, cost-effective and reliable service.
As would be expected of a service provider with considerable experience, variety is expected.
Are you delivering FCL cargo?
Those are shipped out 5 times a week.
LCL?
Twice a week.
Want a door to door service?
You will get it.
Quick Recap of Shipping from China to NZ
Demonstrably, the free trade agreement between China and New Zealand has boosted bilateral trade between the two nations.
Since both nations have well-developed facilities, including, airports, seaports, and transport linkages, exporting/importing into either is fairly hassle-free.
The options, when importing into New Zealand, are plentiful.
In China, you can ship from more than ten ports.
In New Zealand, you can choose from more than 10 ports where you want to pick your goods.
With international shipping companies operating the route, one can expect goods to be delivered promptly.
Alternatively, you can always ask for the goods to be delivered to your doorstep, a really convenient shipping option.
There are a few publicly available rules available on the New Zealand Customs website, and the Ministry of Primary Industries.
These offer critical guidance on what and how to import anything to New Zealand.
Good News?
Macro is here to help you in all shipping from China to NZ.
Talk to us today, and we will provide you with the most cost competitive shipping rates!



